Our Discoveries
International study of rhabdomyosarcoma finds genetic clues, potential for tailored therapy
New findings from the largest-ever international study on rhabdomyosarcoma – the most common type of soft tissue sarcoma in children – suggest that children with the disease could benefit from tumor genetic testing. Javed Khan, M.D., Deputy Chief of the Genetics Branch, led the study.
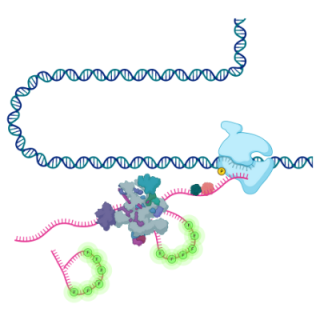
Read MoreLive-cell imaging reveals variability in RNA processing
Real-time imaging of messenger RNA synthesis from hundreds of human genes reveals surprising variability in the way cells’ splicing machinery processes these molecules.
Read MorePersonalized approach to prostate cancer diagnosis could mean less invasive biopsies
Systematic and MRI-guided biopsies can each find cancers that the other technique can miss — but not everyone needs both. According to a new analysis, magnetic resonance imaging can be used to determine which biopsy approach is appropriate for an individual.
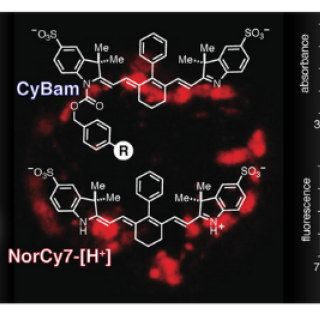
Read MoreNew fluorescent probes developed that can help clinicians pinpoint cancer metastases
New chemical compounds developed by CCR researchers and clinicians are safe and highly effective in fluorescently highlighting microscopic metastases. The new compounds could have great utility in complex living systems based on experiments done in mouse models of metastatic human ovarian cancer.
Read MoreStem cell transplant after CAR T-cell therapy effective for young leukemia patients
In a clinical trial, CCR physician-scientists found that long-term survival for young patients with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia was significantly better for those who received CD19-CAR T-cell therapy followed by a stem cell transplant. As a result of these findings, use of stem cell transplant is now recommended following CAR T-cell therapy.
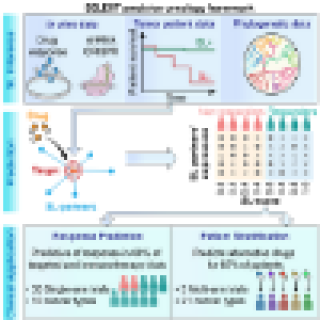
Read MoreNew tool predicts which treatments may work best in cancer patients
A new precision oncology software tool, called SELECT, analyzes tumor transcriptomics data to predict which therapies are most beneficial for an individual patient. When applied to data from over 30 different clinical trials, SELECT was predictive of patient responses to targeted and immune therapies in about 80 percent of the trial datasets.
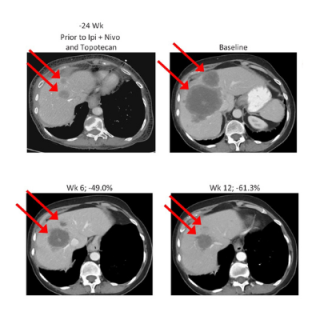
Read MoreDrug combination leads to durable responses in patients with small cell lung cancer
Relapse after chemotherapy is common among patients with small cell neuroendocrine cancers, including small cell lung cancer. In a new clinical study, CCR scientists found a combination of berzosertib and topotecan led to durable tumor responses in patients with these cancers.
Read MoreEngineered myeloid cells have promise as a potential treatment for metastatic cancer
A team led by Rosandra N. Kaplan, M.D., Investigator in the Pediatric Oncology Branch, genetically engineered immune cells, called myeloid cells, to deliver an anti-cancer signal to organs where cancer may spread. The results of the treatment, reported in Cell, shrank tumors and prevented metastasis in mice.
Read MoreFDA grants orphan drug designation to PRGN-2012 for recurrent respiratory papillomatosis
The Food and Drug Administration has granted orphan drug designation to PRGN-2012 immunotherapy for use in patients with recurrent respiratory papillomatosis.
Read MoreCombination therapy in patients with advanced kidney cancer found to be highly effective
A phase III international clinical trial that tested the combination therapy of nivolumab and cabozantinib in patients with advanced, untreated renal-cell carcinoma yielded promising results.
Read More