Our Discoveries
NIH researchers develop AI tool with potential to more precisely match cancer drugs to patients
In a proof-of-concept study published on April 18, 2024, in Nature Cancer, CCR researchers have developed an artificial intelligence (AI) tool that uses data from individual cells inside tumors to predict whether a person’s cancer will respond to a specific drug. The team, led by Eytan Ruppin, M.D., Ph.D., Chief of the Cancer Data Science Laboratory, suggests that such single-cell RNA sequencing data could one day be used to help doctors more precisely match cancer patients with drugs that will be effective in treating their cancer.
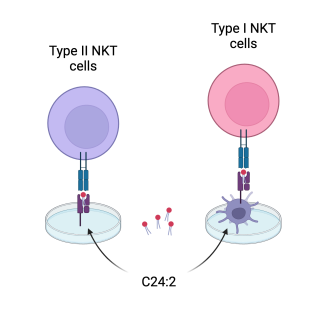
Read MoreCellular processing reverses molecule’s effect on anticancer immunity
Immune cells convert an immunosuppressive lipid into an anticancer immunity enhancer.
Read MoreNew research on liver cell diversity could help scientists understand tumor complexity
Hepatocytes, the main cell type in the liver, differ in function according to their location in the liver. A new study shows that mitochondrial responses to nutrients drive this diversity — a finding that could help researchers better understand tumor cell heterogeneity.
Read MoreNew biomaterial enhances cancer vaccine effectiveness to help eliminate cancer in mice
Scientists have created a new type of cancer vaccine approach that uses a biomaterial that attracts immune cells and localizes the delivery of the vaccines. In mice, the biomaterial combined with a cancer vaccine was able to cure 50 to 75% of their tumors.
Read MoreIndia’s First Homegrown CAR T-Cell Therapy Has Roots in NCI Collaboration
In October 2023, India’s counterpart to the US Food and Drug Administration, the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization, approved NexCAR19, an effective, low-cost CAR-T cell therapy. The development of the therapy was made possible by a years-long collaborative journey between the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay and Tata Memorial Centre in Mumbai with NCI researchers at the NIH Clinical Center. As India’s first approved CAR-T cell therapy, the treatment will be manufactured in Mumbai and is affordable for many.
Read MoreThe liver controls intestinal health through the PEDF protein
A new study reveals how the liver and gut communicate to regulate stem cell expansion in the repair of damaged intestinal tissue. The finding, from the lab of Chuan Wu, M.D., Ph.D., has important implications for a lipid-lowering drug that affects that communication.
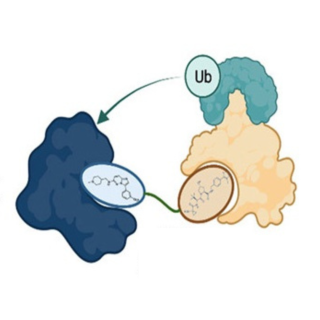
Read MorePROTACtion against resistance of commonly used anti-cancer drug
Drugs known as PIM kinase inhibitors are used to treat a range of cancers, but many patients develop resistance to these medications. Recent research has led to a new class of therapeutics that target the mechanism of this resistance, resulting in increased death of cancer cells.
Read MoreMolecular signature can identify tumor-targeting immune cells in the blood
Blood samples could be a new source of antitumor T cells for customized cancer immunotherapies.
Read MoreNovel T cell stimulation technique drives potent anti-tumor response
Researchers combined an antibody with an immune-signaling molecule resulting in an agent called STAR0602. A version of the novel agent was designed for and tested in mice, which induced significant tumor shrinkage and increased survival across six different types of cancer while exhibiting little toxicity. The promising lab findings have prompted the launch of a clinical trial in people.
Read MoreExperimental vaccine halts respiratory growths from HPV infection
An experimental vaccine that trains a patient’s immune system to recognize HPV-infected cells could potentially be used to treat people with recurrent respiratory papillomatosis, according to results from an ongoing clinical trial.
Read More