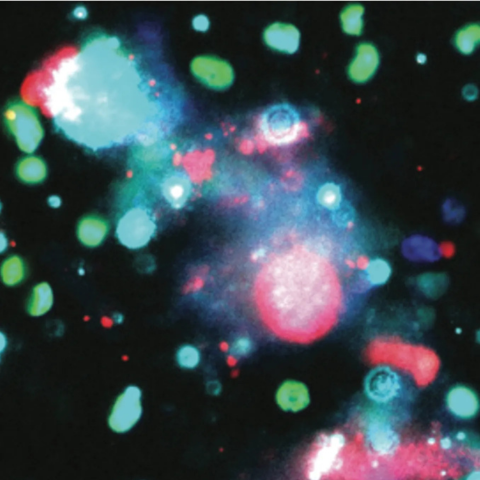
Immunofluorescence image of the cell adhesion protein basigin (turquoise) in TuNEPs released from dying 4T1 mouse breast cancer cells. Image credit: Li Yang
New research from CCR scientists reveals that the composition of material released from dying cancer cells can promote the growth of neighboring cancer cells. The study, led by trainees Justin Gray, Ph.D., and Woo Yong Park, Ph.D., in the laboratory of Li Yang, Ph.D., senior investigator in the Laboratory of Cancer Biology and Genetics, was published in Scientific Reports on August 1, 2025.
While cancer cells are killed by various treatments, a better understanding of how cancer cells die and affect disease progression is crucial for finding more effective treatments. In this study, scientists investigated the makeup of nuclear contents released from dying tumor cells, called tumor cell nuclear expulsion products (TuNEPs). TuNEPs can help other cancer cells grow, but the identity of the specific growth-promoting molecules within TuNEPs was previously unknown.
The researchers found that TuNEPs contain a unique set of proteins that facilitate cell adhesion and RNA binding. These proteins are specific to TuNEPs and are not present in other types of products released from dying cancer cells or from immune cells called neutrophils. Among these proteins, integrin and basigin were able to promote the growth of cancer cell clusters.
Identifying the specific proteins in TuNEPs and understanding their roles could provide new insights into how cancer spreads and lead to novel treatments. By targeting these proteins, scientists hope to develop therapies that can disrupt the growth-promoting effects of TuNEPs, ultimately improving cancer treatment outcomes and patient survival.
Citation: Gray JM, et al. Sci Rep 15:28054. 2025 Aug 01. doi:10.1038/s41598-025-11807-z
Information provided by: Brandi Carofino, Ph.D. and Li Yang, Ph.D.