News and Events
Proteins Released from the Nuclei of Dying Cancer Cells Promote Tumor Growth
Material released from dying cancer cells, known as tumor cell nuclear expulsion products (TuNEPs), contains specific proteins that promote the growth of neighboring cancer cells. Targeting these proteins could lead to new treatments that hinder cancer spread and improve patient outcomes.
Read MoreCCR researchers show testing with combined biopsy method improves prostate cancer diagnosis
A method of testing for prostate cancer developed at the Center for Cancer Research leads to more accurate diagnosis and prediction of the course of the disease, according to a new study published in the New England Journal of Medicine. Peter Pinto, M.D., Investigator in the Urologic Oncology Branch, led the study and says this method, which combines systematic biopsy, the current primary diagnostic approach, with MRI-targeted biopsy, is poised to greatly improve prostate cancer diagnosis, thereby reducing the risk of both overtreatment and undertreatment of the disease. To see all open prostate cancer trials, click here.
Read MoreChristian Hinrichs and Steve Rosenberg receive Federal Laboratory Consortium award
Christian Hinrichs, M.D., Investigator in the Experimental Transplantation and Immunotherapy Branch, and Steve Rosenberg, M.D., Ph.D., Chief of the Surgery Branch, received an award from the Federal Laboratory Consortium for Technology Transfer (FLC) for their project, “New, First-in-class Immunotherapy for Treatment of Recurrent, Metastatic Cervical Cancer.” This award recognizes employees of FLC member laboratories and non-laboratory staff who have accomplished outstanding work in the process of transferring federally developed technology.
Read MoreA new set of genes linked to metastasis in melanoma
CCR researchers have found that melanoma can reactivate gene expression patterns that are usually active in melanoblasts, facilitating their progression to metastatic behavior. These newly discovered melanoblast genes have the potential to provide a new source of pathways that could be tapped to develop new treatments for melanoma.
Read MoreClinical trial studies combination therapy for mesothelin-expressing solid tumors
A clinical trial at the NIH Clinical Center is evaluating a combination therapy for mesothelin-expressing solid tumors. Mesothelin is a protein found on the surface of certain types of normal cells and cancer cells. This trial is studying the effect of LMB-100, a man-made protein attracted to mesothelin, with a drug commonly used to treat certain types of arthritis and colitis.
Read MoreIrinotecan shrinks DNA-repair-deficient breast cancers in patient-derived mouse models
Laboratory studies uncover genetic features that make some triple-negative breast cancers vulnerable to an overlooked treatment option.
Read MoreUdo Rudloff and team develop potential new type of immunotherapy
New research led by Udo Rudloff, M.D., Ph.D., Investigator in the Pediatric Oncology Branch, describes a potential new type of immunotherapy that applies across many types of cancer. The findings were reported in Science Translational Medicine and showed this approach has potential for treating other diseases as well. This work was featured in a recent press release from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences.
Read MoreNew study overturns conventional understanding of how HIV infection occurs
Researchers have succeeded in imaging where and when the protective coating that surrounds HIV is disassembled, a critical step in the viral replication process. Their observations show that the virus keeps its protective coating after entering the nucleus of a cell and then begins replicating, which is counter to what most scientists have thought for decades.
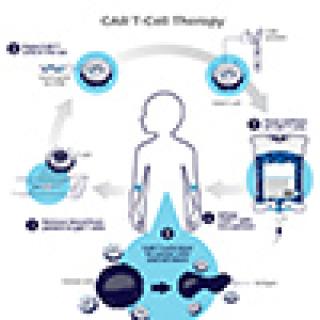
Read MoreJennifer Brudno and James Kochenderfer discuss reduced side effects of remodeled CAR T-cell therapy
Jennifer Brudno, M.D., Assistant Research Physician, and James Kochenderfer, M.D., Investigator, both of the Surgery Branch, discussed their ongoing work to remodel CAR T cells to create a safer, more effective therapy in a recent Cancer Currents blog post. They share that since they tweaked the design of their original CAR T cells, the new therapy caused far fewer neurologic side effects than the original therapy did in an earlier trial but was equally effective.
Read MorePotent new LDHI inhibitor disrupts tumor growth in mice
Researchers have identified a potent LDH inhibitor, which can disrupt the energy production of tumors in mice. After exposure to the LDH inhibitor, the cancers cells began to rely on a different form of energy production, which could also be disrupted by using a second drug. Combining the two drugs had a potent anti-cancer effect.
Read MoreResearchers identify protein essential for assembling cells’ energy-producing machine
CCR researchers have discovered that the protein Bcs1 acts as the element that facilitates the transport of iron-sulfur protein, or ISP, across the inner membranes of mitochondria, the cell’s power plant. ISP is needed for the assembly of Complex III, a key element of the respiratory chain, which ensures that nutrients are converted to ATP, energy that cells need.
Read More