Chuan Wu, M.D., Ph.D.
- Center for Cancer Research
- National Cancer Institute
- Building 10, Room 4B17
- Bethesda, MD 20892-1360
- 240-858-3366
- chuan.wu@nih.gov
RESEARCH SUMMARY
It has become increasingly evident that interactions between the enteric nervous system (ENS) and the immune system play important roles to modulate inflammatory responses. Such interaction is particularly critical in the context of the intestinal microenvironment given the unique properties of this organ: intestinal tissue is continuously exposed to numerous microbial and food-derived antigens. In order to deal with these stimuli yet maintain normal physiology and function, intestinal responses are tightly regulated by actions of both the immune and nervous systems, which co-localize in the intestinal microenvironment with close proximity. Our lab mainly studies the role of intestinal neuroimmune interactions in health and disease. Understanding the cellular and molecular mechanisms of the dynamic interplay between the ENS and the immune system is critical for retrieving a comprehensive view of intestinal homeostasis and for discovering new therapeutics for intestinal inflammatory diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Areas of Expertise

Chuan Wu, M.D., Ph.D.
Research
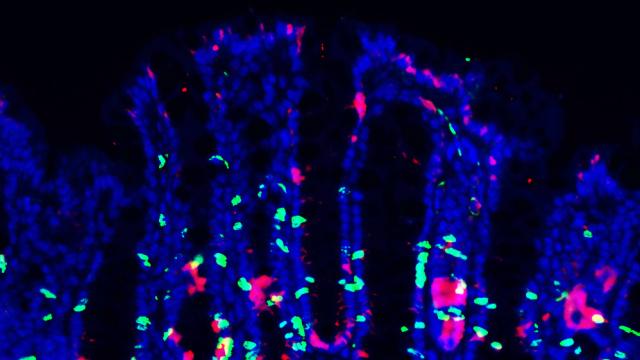
1. Immune-neuron crosstalk regulates gut sensation.
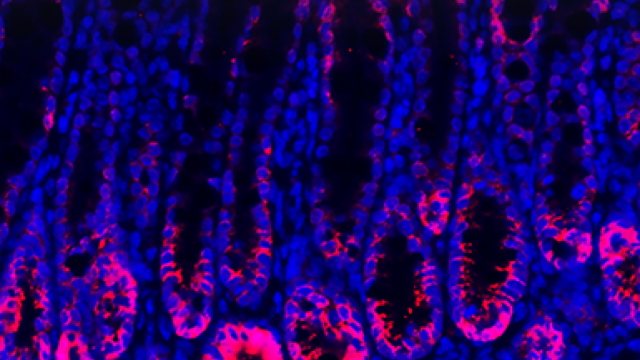
The intestinal epithelium represents the largest interface which protects the body from potential danger while sensing external milieu. Given that the gut also functions as a major endocrine organ, the efficient translation from environmental cues to neuroendocrine responses is essential for body physiology. By harboring large quantities of microbiota and immune cells, the intestinal tissue is filled with a variety of immune regulators. While certain receptors have been identified to detect different environmental stimuli such as microbial metabolites, irritants, mechanical stress, it is still unclear whether and how immune signals participate in gut sensation to enforce intestinal homeostasis and host defense. We are studying how immune signals integrate into neural regulation for gut sensation during intestinal homeostasis and inflammation.
2. Reciprocal regulations between intestinal epithelium barrier and gut microbiota.
The gastrointestinal (GI) tract is colonized by millions of microbes which have co-evolved with the host. The intestinal epithelium barrier forms the first line of defense against bacterial invasion while providing nutrition to support microbial symbiosis. In turn, gut commensalism controls intestinal barrier integrity and gut physiology. Disruption of this mutualism results in enhancing susceptibility to intestinal inflammation. How such reciprocal interactions modulate intestinal host-microbial symbiosis for barrier function is unclear. We aim to understand the role of host-microbial crosstalk for intestinal barrier function, which could provide new therapeutic targets for the treatment of IBD.
Publications
- Bibliography Link
- View Dr. Wu's Complete Bibliography at NCBI.
Biography

Chuan Wu, M.D., Ph.D.
Dr. Wu earned his M.D. from Shanghai Jiaotong University, School of Medicine, and subsequently pursued his Ph.D. training at Münster University, Germany, where he focused on T cell migration in the context of inflammation and autoimmunity. He later completed his postdoctoral training at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, concentrating on the transcriptional regulation of T cell differentiation. After joining the NCI, Dr. Wu redirected his research focus toward exploring the intercellular regulation of mucosal barrier integrity. His laboratory adopts an interdisciplinary approach to unravel the complex interactions between the nervous system, microbial pathogens, and the immune system in both physiological and pathophysiological contexts, with the ultimate goal of developing innovative therapies for immune-mediated diseases.
Job Vacancies
We have no open positions in our group at this time, please check back later.
To see all available positions at CCR, take a look at our Careers page. You can also subscribe to receive CCR's latest job and training opportunities in your inbox.
Team
News
Covers

Restraint of IFN-γ expression through a distal silencer CNS–28 for tissue homeostasis
We report the identification of a negative regulatory element (CNS–28) that restrains IFNγ expression to ensure tissue homeostasis. CNS–28 forms a local 3D domain with two other regulatory elements, CNS–22 and CNS–34, in a manner dependent on the transcription factors MLL4 and GATA3; this structure prevents activation of Ifng transcription by the CNS–22 enhancer. The positive and negative mechanisms regulating expression of IFNg is depicted by the Taiji figure. Ifng genomic DNA (red ribbon) is embedded within repressive 3D chromatin (Yin; flower in the dark side) and activating 3D chromatin (Yang; flower in the light side). Illustration by Qinglan Emily Yu at the Bryn Mawr School.
https://www.cell.com/immunity/fulltext/S1074-7613(23)00126-7

Mucus sialylation determines intestinal host-commensal homeostasis
Sialylation is critical for intestinal mucus formation. Yao et al. (1172–1188) show that a local sialyltransferase in the gut, ST6GALNAC1 (ST6), determines mucin protein sialylation, protecting mucus barrier integrity from bacterial degradation. ST6-mediated mucus homeostasis in turn controls commensalism to establish intestinal host-microbial symbiosis. ST6 deficiency disrupts this mutualism, enhancing susceptibility to intestinal inflammation. The cover image illustrates that sialylated mucin proteins (saguaros with thorns) harbor symbiotic commensal bacteria (gilded flickers), protecting the intestinal tissue from pathogens (snakes and hawks). Loss of sialylation (saguaros without thorns) results in pathogenic bacteria invasion (snakes). Illustration concept by Chuan Wu and artwork by Alan Hoofring.
https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(22)00193-3

Galectin-9-CD44 interaction enhances stability and function of adaptive regulatory T cells
Galectin-9 can dampen autoimmune responses, and this process is associated with an increase in the frequency of inducible regulatory T (iTreg) cells. We show that galectin-9 potentiates the signal transduction of transforming growth factor βR (TGF-βR), a critical receptor for iTreg cell differentiation. Potentiation results in increased activation of Smad3 with subsequent enhanced transcription of the iTreg cell differentiation factor, FoxP3. The cover image illustrates T lymphocytes emerging from a microenvironment (represented by a fabricator) influenced by the presence of TGF-β. With assistance from galectin-9 and its receptor CD44, the differentiation process to iTreg cells is enhanced. Image by Chuan Wu.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1074761314002325
Resources
PIERCING THE CELL: New clues about autoimmunity revealed
A team of scientists has been carefully studying changes over time in one type of immune cell -- known as a T helper 17 or Th17 cell. Their analysis led them to an unlikely suspect in the study of autoimmune diseases: salt.
In this video (created when Dr. Wu was a postdoctoral fellow in Dr. Vijay Kuchroo's laboratory, Brigham and Women's Hospital), seven team members from the Broad Institute's Klarman Cell Observatory, Brigham and Women's Hospital, MIT, and Harvard University describe how their approach led them to this unexpected result.
View the video at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t6lsucTFnB4