Genetically Engineered Mouse (GEM) Model
- Developed in house
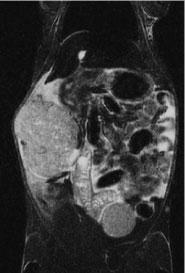
Scan showing SEOC in a GEM model - Genetic aberrations:
- Inactivation of Rb tumor suppression (via K18-T121 transgene)
- Tp53 loss or mutation (R172H)
- Brca1 or Brca2 loss
- Induction by injection of adenovirus expressing Cre recombinase under the ovarian bursa
- Pathology:
- Serous epithelial ovarian cancer (SEOC)
- Peritoneal carcinomatosis
- Distal metastases (lung, liver)
- Ascites
- Latency: 8-12 months (high grade tumor)
- Metabolomic and gene expression profile aligns with human SEOC
- Pertubation of Rb, p53 and Brca1 or Brca2 cooperate in inducing metastatic serous epithelial ovarian cancer (Szabova et al., Cancer Research 2012)
Orthotopic Allograft Model
- Derived from genetically engineered mouse ovarian tumors
- Ovarian tumor transplant to wild-type recipient mice
- Genetic aberrations:
- Inactivation of Rb tumor suppression (via K18-T121 transgene)
- Tp53 loss or mutation (R172H)
- Bra1 or Brca2 loss
- Pathology:
- Serous epithelial ovarian cancer (SEOC)
- Peritoneal carcinomatosis
- Distal metastases (lung, liver)
- Ascites
- Latency: 1-3 months
- Molecular profile aligns with human SEOC
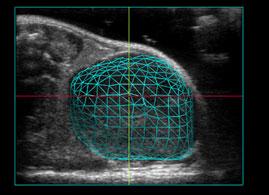
- Ultrasound imaging
- Differential response to therapeutics in Brca1-deficient versus Brca1 wild-type tumors
- Pathway-specific engineered mouse allograft models functionally recapitulate human serous epithelial ovarian cancer (Szabova et al., PloS One 2014)