EGFR-driven models
-
Development of optimal workflows for therapeutic assessment in inducible transgenic models that develop lung adenocarcinoma.
-
Contain a human EGFR transgene (either TRE-EGFR-L858R or TRE-EGFR-L858R-T790M) and an activating transgene (CCSP-rtTA) to direct expression of mutant EGFR to the Clara cells.
-
Tumors expressing the EGFR L858R mutation are sensitive to first-generation EGFR inhibitors; tumors expressing the EGFR L858R and T790M mutations are resistant.
-
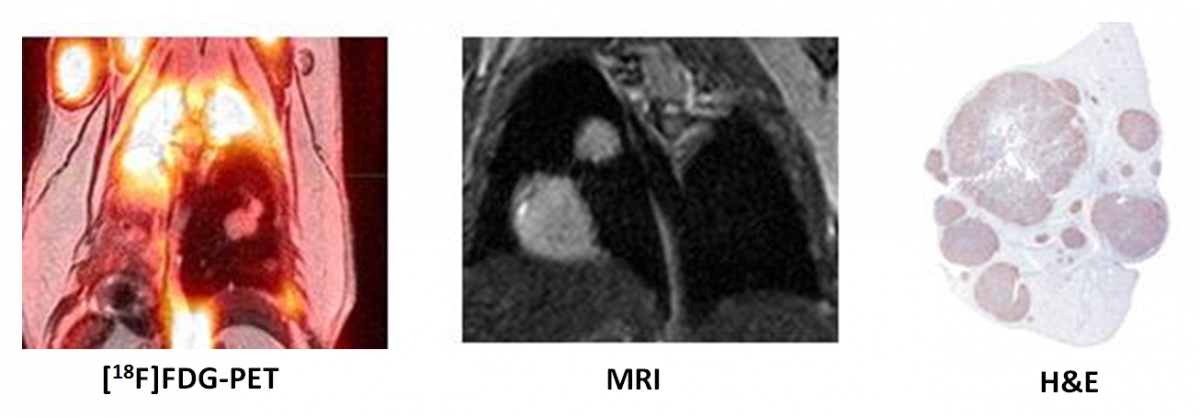
Tumor development and response to drug are monitored by MRI or CT scanning.
-
PK/PD of novel therapeutics, efficacy, metabolomic and gene expression profiling of tumor progression and response to treatment, drug resistance studies, and evaluation of in vivo imaging probes are routinely performed in these models.
-
Temporal molecular and biological assessment of an erlotinib-resistant lung adenocarcinoma model reveals markers of tumor progression and treatment response (Weaver et al., Cancer Research 2012).
-
Discovery of a mutant-selective covalent inhibitor of EGFR that overcomes T790M-mediated resistance in NSCLC (Walter et al., Cancer Discovery 2013).
EML4-ALK-driven model
Ras-driven model
-
Evaluation of novel therapeutics in inducible models of Kras-driven lung adenocarcinoma.
-
Lung-specific tumor induction is achieved by intratracheal instillation of adenoviral Cre to drive recombination of KrasG12D and p53 alleles.
-
Lung tumorigenesis is accelerated when p53 is also inactivated.
-
Adenocarcinoma develops 6-24 weeks post-induction depending on allele combination. Models may contain p53 deletion alleles or p53 point mutations.
-
LKb1-deficient tumors are also available for preclinical studies: lung tumorigenesis is accelerated when Lkb1 is inactivated, and tumors display mixed squamous and adenocarcinoma histology.
-
Allograft models have been established.
-
Tumor development and response to drug are monitored by MRI or CT scanning.
-
The differential effects of mutant p53 alleles on advanced murine lung cancer (Jackson et al., Cancer Research 2005).
-
LKB1 modulates lung cancer differentiation and metastasis (Ji et al., Nature 2007).