Christian T. Mayer, Ph.D.
- Center for Cancer Research
- National Cancer Institute
- Building 10, Room 4B11
- Bethesda, MD 20892-1360
- 240-858-3340
- christian.mayer@nih.gov
RESEARCH SUMMARY
Dr. Mayer’s laboratory is interested in mechanisms of immune regulation, particularly the role of cell death in self-tolerance and adaptive immunity. His current research program focuses on unraveling the regulatory networks controlling cell death and determining their roles in immune cell development, differentiation and function in part by using a novel apoptosis reporter mouse he developed. These studies serve to increase our fundamental understanding of immune responses and of how defects in immune regulation might contribute to diseases. The long-term goals are to identify new therapeutic strategies to (1) inhibit unwanted immune responses, (2) enhance immune responses against tumors and pathogens.
Areas of Expertise

Christian T. Mayer, Ph.D.
Research
Self-tolerance regulation by apoptosis
A diverse set of T- and B cell receptors orchestrates adaptive immunity and immunological memory. In B lymphocytes, this diversity is created by two relatively random processes: variable diversity and joining gene segment (V(D)J) recombination in the bone marrow during development, and somatic hypermutation in germinal center B cells during adaptive immune responses. Self-reactive receptors are frequent byproducts of these processes and lymphocytes carrying those receptors must be controlled by various mechanisms in order to avoid the production of autoantibodies and the attack of the own body by the immune system. We will interrogate the specific role of apoptosis in controlling self-reactive lymphocytes by combining genetic tools with single-cell methods. Another goal is to determine at which lymphocyte differentiation- or activation stages this censoring occurs.
Regulation of immune responses by cell death
Adaptive immunity relies on a tightly regulated control of the number and activity of different types of immune cells, and both parameters undergo dynamic changes during an immune response. One mechanism to regulate cell number and activity is cell death. While apoptosis is the best-known type of programmed cell death, it is becoming increasingly clear that other types of programmed cell death (e.g. pyroptosis, necroptosis) might also contribute to immune regulation. How each of these pathways are triggered in some cells while others survive within the same microenvironment is poorly understood, as is the exact functional role of each deletion mechanism. We aim to gain a better understanding of how different types of cell death in different types of cells regulate the kinetics, magnitude, longevity, or other characteristics of immune responses.
Disease and therapy relevance of immune regulation
While defective immune regulation can precipitate autoimmune diseases, excessive immune suppression can hinder immunity to microbes and tumor cells. The mechanisms and networks coordinating this delicate balance are insufficiently understood. We will determine if and how deregulated cell death is linked to inflammatory/autoimmune diseases and cancer, or to defective responses to vaccines and cancer immunotherapies. To achieve this goal, we employ animal disease models and novel genetic tools to manipulate cell death in a cell-type specific fashion. The long-term aim is to identify new immunoregulatory pathways that offer opportunities for targeted positive and negative regulation of immune responses.
Publications
- Bibliography Link
- View Dr. Mayer's Complete Bibliography at NCBI.
An apoptosis-dependent checkpoint for autoimmunity in memory B and plasma cells.
The microanatomic segregation of selection by apoptosis in the germinal center
T cell help controls the speed of the cell cycle in germinal center B cells.
Selective and efficient generation of functional Batf3-dependent CD103+ dendritic cells from mouse bone marrow
Biography

Christian T. Mayer, Ph.D.
Dr. Mayer received his Ph.D. in immunology from the Hannover Medical School, Germany, working on immune tolerance and regulatory T cell biology with Tim Sparwasser. He then joined Michel Nussenzweig’s laboratory as a postdoctoral fellow at The Rockefeller University, New York, where he developed new tools to study the regulation of antibody responses. Dr. Mayer started a position as a NIH Stadtman Tenure-Track Investigator at the Experimental Immunology Branch in 2020 where he explores immunoregulatory networks, particularly those involving cell death, in health and disease. He received several early career awards including the Fritz-and-Ursula-Melchers Postdoctoral Prize 2014 (German Society for Immunology), the Early Career Research Prize in Vaccinology 2018 (International Union of Immunological Societies) and the postdoctoral award in immunology 2018 by the Robert Koch Foundation.
Job Vacancies
We have no open positions in our group at this time, please check back later.
To see all available positions at CCR, take a look at our Careers page. You can also subscribe to receive CCR's latest job and training opportunities in your inbox.
Team
News
Learn more about CCR research advances, new discoveries and more
on our news section.
Lab Life
EIB BBQ 2022

Lab Trivia Night 1

Lab Trivia Night 2
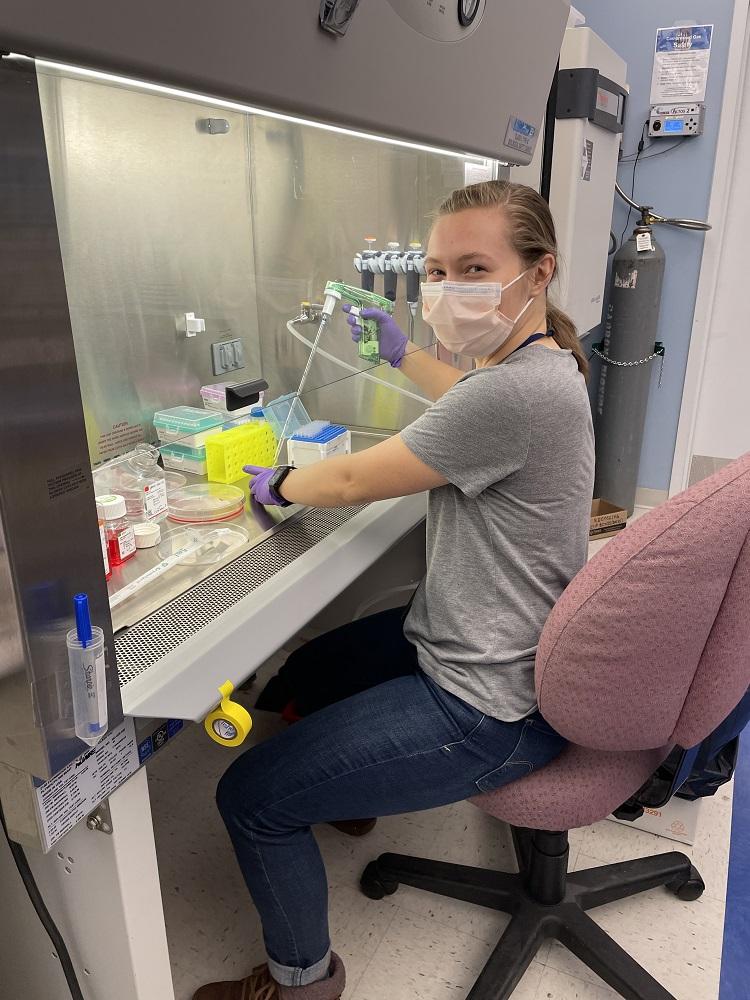
Mikala splitting cells
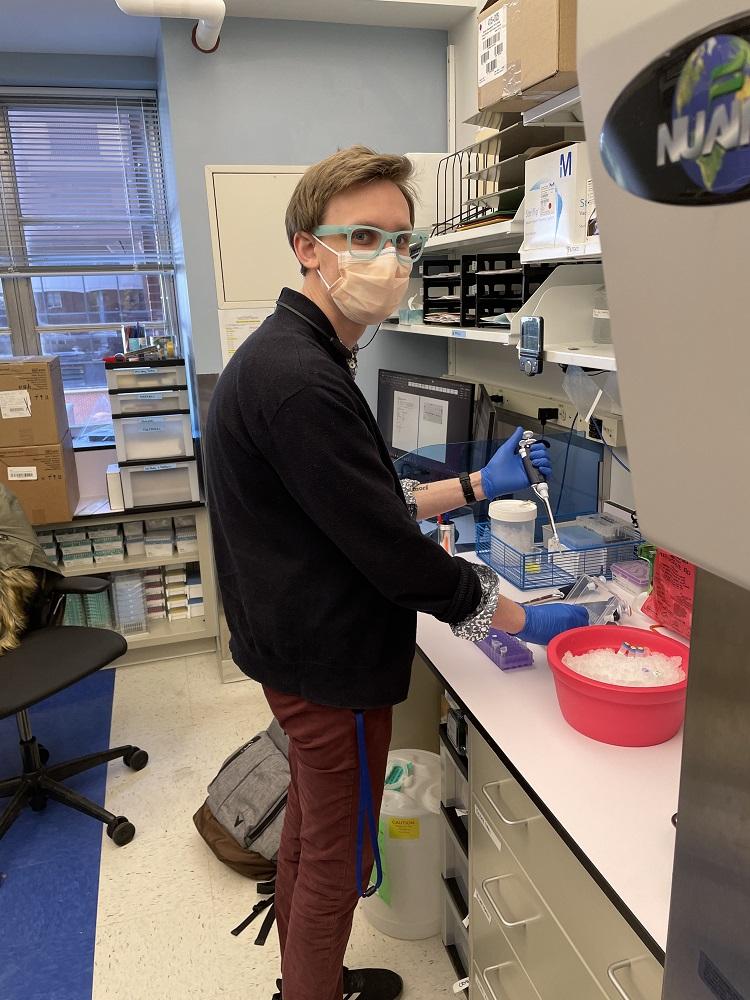
Chris setting up a PCR