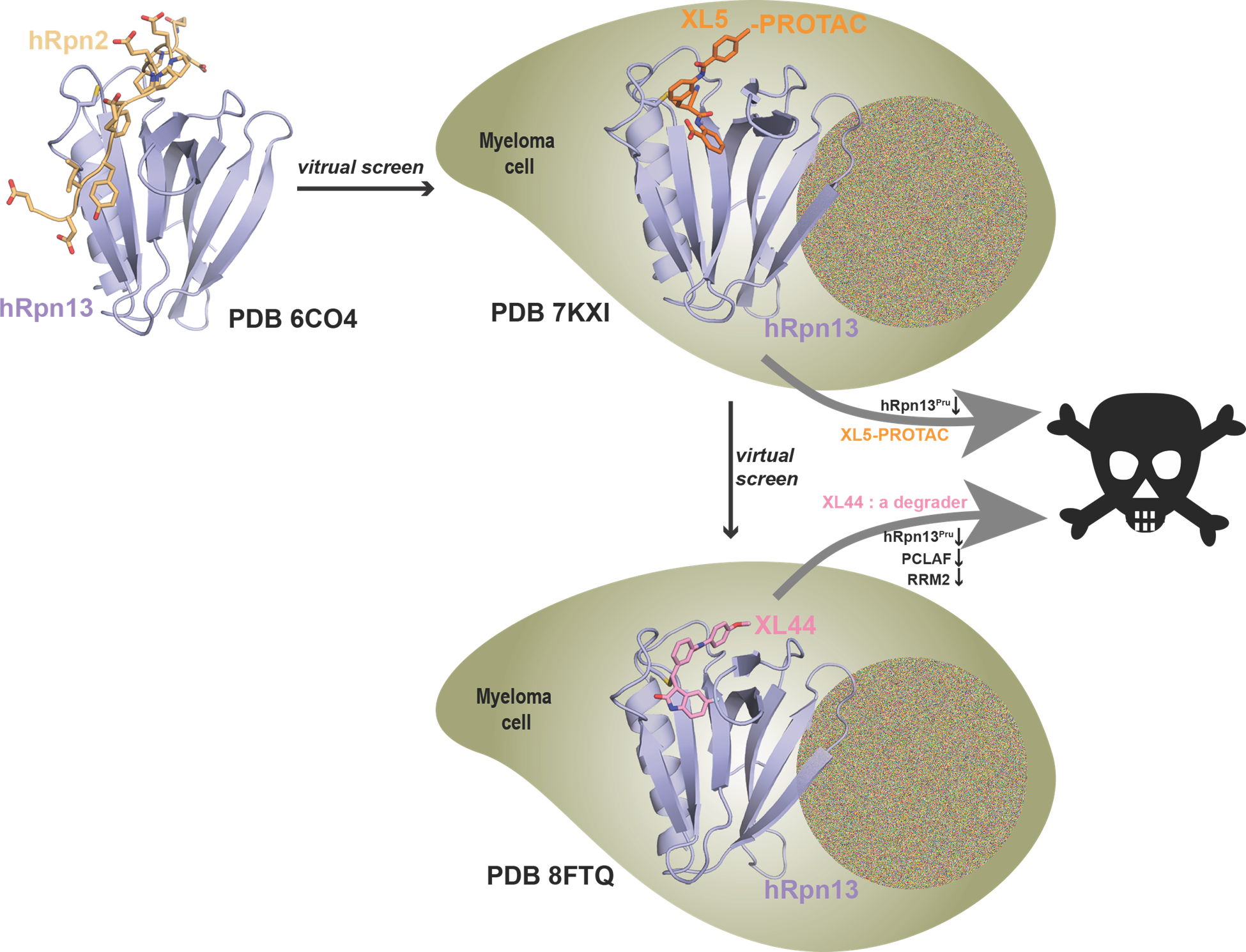
The NMR structure of hRpn13 Pru (periwinkle blue) with hRpn2 (940-953) (light orange) (PDB 6CO4; Lu, X. et al. Nat Commun. 2017 8, 15540) was used for a virtual screen to identify a new hRpn13-targeting scaffold with lead compound XL5. The NMR structure of XL5 (orange)-ligated hRpn13 Pru (periwinkle blue) (PDB 7KXI; Lu, X. et al. Nat Commun. 2021 12, 7318) was then used to design XL5-derived hRpn13 PROTACs including XL5-VHL-2. These PROTACs led to the discovery of an hRpn13 proteolytic product with an intact Pru domain (hRpn13Pru). hRpn13Pru is upregulated in myeloma patients and required for XL5-VHL-2 induced apoptosis (Nat Commun. 2021 12, 7318). To identify a more potent hRpn13-targeting compound, the hRpn13 Pru-XL5 structure was used in a covalent-docking screen to surprisingly identify the hRpn13 degrader XL44. The structure of XL44 (pink)-ligated hRpn13 Pru (periwinkle blue) was solved by integrated X-ray crystallography and NMR (PDB 8FTQ; Lu, X. et al. Nat Commun. 2024 15, 2485). In addition to degrading hRpn13Pru, XL44 also degrades a select few KEN-box proteins, including PCLAF and RRM2. However, XL44-induced apoptosis is hRpn13-dependent.